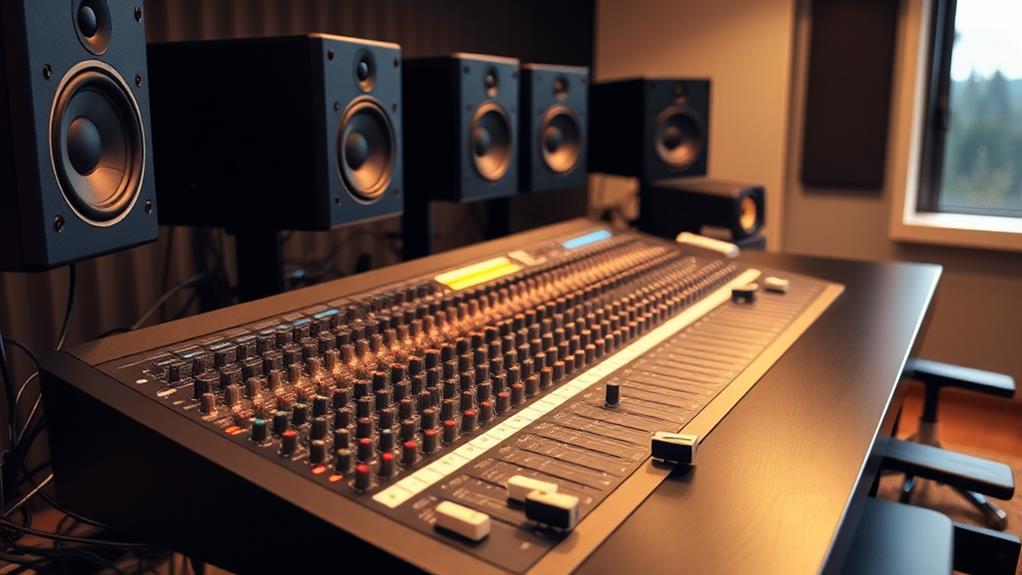
An audio mixer is an essential tool for blending multiple sound sources into a cohesive output. You’ll find mixers in recording studios, live venues, and broadcast facilities. They come in various sizes and types, including analog, digital, and hybrid models. Key components include input channels, preamps, EQ controls, faders, and auxiliary sends.
As a beginner, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with gain staging, EQ adjustment, and basic effects like compression. Mixers are used across industries, from music production to corporate events.
Mastering the fundamentals of mixing techniques will allow you to create professional-sounding audio for various applications. The world of audio mixing offers endless possibilities for sonic creativity.
Main Points
- Audio mixers combine multiple audio signals and are essential for professional sound production.
- Key components include input channels, faders, pan controls, auxiliary sends, and metering displays.
- Mixers come in analog, digital, and hybrid types, each with distinct advantages for different uses.
- Basic mixing techniques involve setting proper gain levels, using EQ, applying compression, and panning.
- Mixers are used in various industries, including recording studios, live music venues, and broadcasting.
What Is an Audio Mixer?
An audio mixer is an essential piece of equipment in sound production. It’s a device that allows you to combine multiple audio signals, adjust their levels, and create a balanced output.
You’ll find mixers in recording studios, live music venues, and broadcasting facilities. They come in various sizes, from small portable units to large-format consoles. For those setting up a home studio, choosing the right mixer is vital for achieving professional-quality results.
At its core, a mixer has multiple input channels where you can connect microphones, instruments, or other audio sources. Each channel typically includes controls for volume, equalization (EQ), and effects.
The EQ lets you adjust the tonal balance of each input, while effects like reverb or compression can enhance the sound. You’ll also find auxiliary sends, which allow you to create separate mixes for monitors or effects processors.
The main output section of the mixer is where you’ll control the overall volume and balance of your combined signals. Many mixers also feature subgroups, allowing you to organize and control multiple channels together.
Understanding how to use a mixer effectively is vital for achieving professional-sounding results in any audio production scenario.
Key Components of Audio Mixers

To fully grasp how audio mixers work, you’ll need to understand their key components. At the heart of any mixer are its input channels, where audio signals from various sources enter the device.
Each channel typically includes a preamp to boost weak signals, gain controls to adjust input levels, and equalization (EQ) controls for shaping the sound’s frequency response. For young creators, audio mixers for kids often feature simplified controls and colorful designs to make learning easier and more engaging.
The mixer’s faders, or volume sliders, allow you to adjust the level of each channel individually. You’ll find a master fader that controls the overall output volume. Pan controls let you position sounds in the stereo field, while auxiliary sends route signals to external effects or monitors. The mixer’s summing bus combines all the adjusted signals into a single output.
Many mixers feature built-in effects processors, allowing you to add reverb, delay, or other effects without external equipment. Metering displays provide visual feedback of signal levels, helping you avoid distortion.
Some mixers include digital interfaces for connecting to computers or recording devices. Understanding these components will enable you to navigate and utilize audio mixers effectively, whether you’re working in live sound reinforcement or studio recording environments.
Types of Audio Mixers

Audio mixers come in several types, each designed for specific applications and environments. The most common types include analog, digital, and hybrid mixers. Analog mixers use traditional electrical circuits to process audio signals, offering a warm, natural sound that many professionals prefer.
They’re often simpler to operate but may lack advanced features. For those looking to enhance their streaming setup, choosing the right audio mixer can considerably improve sound quality and control.
Digital mixers, on the other hand, convert audio signals into digital data for processing. They provide more flexibility, built-in effects, and the ability to save and recall settings.
You’ll find them in many modern studios and live sound setups. Hybrid mixers combine elements of both analog and digital technology, aiming to offer the best of both worlds.
For smaller setups, you might consider compact or portable mixers. These are ideal for podcasting, small performances, or field recording.
Rackmount mixers are designed to fit into standard equipment racks, making them suitable for permanent installations. Large-format consoles, used in professional recording studios and major live events, offer the most extensive features and channel counts.
Each type has its strengths, and your choice will depend on your specific needs, budget, and technical requirements.
Basic Mixing Techniques

Understanding basic mixing techniques is vital for anyone working with audio equipment. As you begin your journey into audio mixing, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with key concepts like gain staging, EQ, compression, and panning.
These fundamental skills form the backbone of professional sound engineering and can greatly improve the quality of your audio productions. For aspiring podcasters, investing in quality audio mixers is essential to achieve professional-sounding results.
When working with an audio mixer, consider these basic techniques:
- Set proper gain levels for each input channel to avoid distortion
- Use EQ to shape the tonal characteristics of individual sounds
- Apply compression to control dynamics and achieve consistency
- Pan audio sources to create a sense of space in the stereo field
Start by adjusting the gain for each input, ensuring signals are strong but not clipping. Next, use EQ to enhance or reduce specific frequencies, helping each element sit well in the mix. Compression can be applied to even out volume fluctuations and add punch to your tracks.
Finally, use panning to distribute sounds across the stereo spectrum, creating width and depth in your mix. Remember, these techniques require practice and experimentation to master, so don’t be afraid to make mistakes and learn from them.
Applications in Various Industries

In light of their versatility, audio mixers find applications across a wide range of industries. You’ll encounter these devices in recording studios, where they’re essential for blending multiple audio sources into a polished final product.
Live music venues rely on mixers to balance sound levels from various instruments and vocalists, ensuring a clear and enjoyable performance for the audience. For those looking to elevate their sound, audio mixers are must-have tools for live events, offering precise control and superior audio quality.
In the broadcast industry, both radio and television stations use mixers to combine audio from different sources, such as hosts, guests, and pre-recorded segments.
You’ll also find audio mixers in corporate settings for conferences and presentations, where they’re used to manage multiple microphones and audio-visual inputs. Houses of worship often employ mixers to balance vocals, instruments, and playback for services and events.
In the film and video production industry, mixers are essential for capturing and balancing on-set dialogue, ambient sound, and music. Even in educational institutions, you’ll see mixers used in lecture halls and auditoriums to manage audio for large gatherings.
These diverse applications demonstrate how audio mixers have become indispensable tools across many sectors, enabling precise control and manipulation of sound in various professional contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Should I Expect to Spend on a Beginner-Friendly Audio Mixer?
You can expect to spend between $100 and $300 on a beginner-friendly audio mixer. Entry-level analog mixers typically range from $100 to $200, while basic digital mixers start around $250. These mixers usually offer 4 to 8 input channels, which is sufficient for most beginners. Keep in mind that higher-priced models often include additional features like built-in effects, USB connectivity, and better sound quality. It’s important to evaluate your specific needs and budget when making your selection.
Can I Use My Audio Mixer With Digital Audio Workstations (Daws)?
Yes, you can use your audio mixer with digital audio workstations (DAWs). Most modern mixers feature USB or FireWire connectivity, allowing you to integrate them seamlessly with your computer and DAW software. This connection enables you to record multiple audio channels simultaneously and use your mixer as an audio interface. You’ll need to install the appropriate drivers and configure your DAW settings to recognize the mixer. Some mixers even offer specialized DAW control features, enhancing your workflow and productivity.
How Often Should I Clean and Maintain My Audio Mixer?
You should clean and maintain your audio mixer regularly to guarantee peak performance. Aim to dust the surface weekly using a soft, dry cloth. Every few months, perform a deeper cleaning, focusing on faders, knobs, and connectors. Use specialized contact cleaners for electronic components. If you’re in a dusty environment or use the mixer frequently, increase cleaning frequency. Always consult your mixer’s manual for specific maintenance instructions, as some models may have unique care requirements.
Are There Any Safety Precautions I Should Take When Using an Audio Mixer?
When using an audio mixer, you should take several safety precautions. Always verify your hands are dry before touching any controls or plugging in cables. Don’t overload power outlets, and use surge protectors when possible. Keep liquids away from the mixer to prevent spills and potential electrical hazards. Be cautious of tripping hazards from cables, and secure them properly. Regularly inspect your equipment for signs of wear or damage. When not in use, turn off and unplug the mixer to conserve energy and reduce fire risks.
Can I Upgrade Individual Components of My Audio Mixer Over Time?
You can upgrade some components of your audio mixer over time, but it depends on the specific model and design. Many mixers allow you to replace faders, knobs, and sometimes even preamps or channel strips. However, core components like the main circuit board typically can’t be upgraded. You’ll need to consult your mixer’s manual or contact the manufacturer to determine which parts are user-replaceable. Keep in mind that upgrades may void warranties, so proceed with caution.